The Balance Sheet Describes a Family's Financial Position:
What is the Residue Sheet Assay?
Rest canvass assay is the assay of the avails, liabilities and owner'due south capital of the company by the different stakeholders for the purpose of getting the correct financial position of the business organization at a detail betoken in fourth dimension.
Information technology is a complete analysis of items on the balance canvass at the various intervals of time, like quarterly, annually, and is used by shareholders, investors, and institutions to understand the company's detailed financial position. The following Balance Sheet Analysis provides an outline of the most common used by investors and financial analysts to clarify a company . It is impossible to provide a complete set of analysis that addresses every variation in every situation since there are thousands of variables.
In this article, we take divided our analysis into ii parts –
- #i -Analysis of Assets
- #2 – Analysis of Liabilities

You are gratis to use this paradigm on your website, templates etc, Delight provide the states with an attribution link Article Link to exist Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Residue Sheet Analysis (wallstreetmojo.com)
Permit united states hash out each one of them in detail –
#1 – How to do Analysis of Assets in the Balance Sheet?
Assets include stock-still assets or Non-current assets and electric current avails.
A) Non-Current Asset
Non-electric current assets Non-current assets are long-term assets bought to employ in the business, and their benefits are likely to accrue for many years. These Avails reveal information virtually the visitor'due south investing activities and tin be tangible or intangible. Examples include property, constitute, equipment, land & building, bonds and stocks, patents, trademark. read more than include the items of fixed assets like property found & equipment (PPE). The analyses of stock-still assets involve non only the calculation of the assets' earning potential and its apply simply too the calculation of its useful life. The efficiency of fixed assets can exist analyzed past calculating the fixed asset turnover ratio.
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio
This ratio is of more than significance to the manufacturing industry as compared to the other industries as there is a substantial purchase of property, plant & equipment in the manufacturing concern to become the required output.
The Formula of Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio The fixed nugget turnover ratio formula determines the ability of a business entity to generate revenue past employing its stock-still avails. It is computed as the fraction of net sales and average net fixed assets. read more than –
Stock-still Avails Turnover Ratio = Net sales/Average Fixed Assets
Where,
- Cyberspace sales are sales less returns and discounts
- And boilerplate stock-still assets = (opening stock-still avails + closing stock-still assets) / ii
For example, Tricot Inc. reported its sales for the financial year 2018-nineteen every bit $400,000, and out of these sales returned were $4,000. Also, information technology reported its total property, establish, and equipment (PPE) equally on 31st March 2022 as $200,000. The balance of PPE as of 1st Apr 2022 was $160,000.
- Now net sales Net sales is the revenue earned by a company from the auction of its appurtenances or services, and it is calculated by deducting returns, allowances, and other discounts from the visitor's gross sales. read more = $400,000 – $twoscore,000 = $360,000
- Average fixed assets =($160,000 + $200,000)/2 =$180,000
Then, Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio will be –
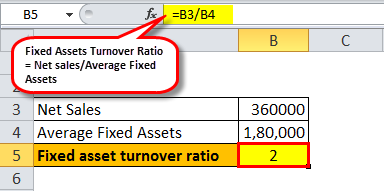
This ratio reflects how efficiently the management of the company is using its substantial fixed assets in generating the revenue of the house. Higher the ratio, the higher is the efficiency of the fixed assets.
B) Electric current Assets
Current assets Current assets refer to those short-term assets which can be efficiently utilized for business organisation operations, sold for immediate cash or liquidated within a year. Information technology comprises inventory, cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, etc. read more than are such assets that are probable to be converted into cash within a year. The current assets include greenbacks, account receivable, and inventories.
The ratios which help in the analysis of current avails are
Electric current Ratio
It is a liquidity ratio that measures the power of the visitor to pay off its short term debts.
The formula for the current ratio is:
Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities
Where
- Current avails = Cash & Cash equivalents + Inventories + Accounts receivable Accounts receivables is the money owed to a concern by clients for which the business has given services or delivered a product just has non still collected payment. They are categorized equally current assets on the balance sheet as the payments expected within a year. read more + other assets that tin can exist converted into cash within a year;
- Current Liabilities = Accounts payable Accounts payable is the amount due by a business concern to its suppliers or vendors for the purchase of products or services. It is categorized as current liabilities on the balance canvas and must be satisfied inside an accounting period. read more than + short term debt+ electric current portion of long term debt Electric current Portion of Long-Term Debt (CPLTD) is payable within the next year from the date of the residue sail, and are separated from the long-term debt every bit they are to be paid within adjacent year using the visitor's cash flows or by utilizing its current assets. read more
Quick Ratio
It is a liquidity ratio that measures the short term liquidity position of the company by computing the ability of the visitor to pay off its electric current liabilities with the use of its most liquid assets.
The formula of Quick Ratio
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets/ Current Liabilities
- Where, quick assets = Greenbacks & cash equivalents + Accounts receivable + other brusk term assets Curt term assets (also known as current assets) are the assets that are highly liquid in nature and tin be hands sold to realize money from the market. They have a maturity of fewer than 12 months and are highly tradable and marketable in nature. read more
- Current liabilities = Accounts payable + short term debt + current portion of long term debt
Instance: Microsoft Inc. is a manufacturing concern which reported the following items in the balance sheet:

At present the Total electric current assets = $10,000 + $6,000 + $xi,000 + $3,000 = $xxx,000
- Quick assets Quick Assets are assets that are liquid in nature and can exist converted into greenbacks easily by liquidating them in the market. Fixed deposits, liquid funds, marketable securities, bank balances, and so on are examples. read more = $ten,000+ $11,000 = $21,000
- Total electric current liabilities = $eight,000 + $seven,000 = $fifteen,000
- Therefore, current ratio The current ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures how efficiently a company tin repay it' short-term loans within a year. Current ratio = current avails/current liabilities read more = $30,000/$15,000 = 2:1
Then, Quick Ratio will exist –
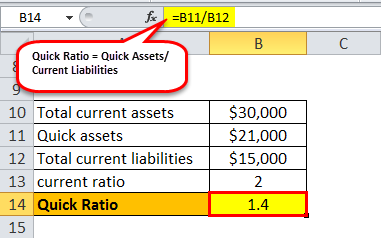
Quick ratio = $21,000/$15,000 = 1.4:ane
C) Cash
Investors are more than attracted towards the company who is having plenty of cash reported on their balance canvas A balance sheet is 1 of the fiscal statements of a company that presents the shareholders' equity, liabilities, and assets of the company at a specific point in fourth dimension. It is based on the bookkeeping equation that states that the sum of the total liabilities and the owner's capital equals the full avails of the company. read more as the cash offers security to the investors because it can be used in the tough times. Increasing cash yr to year is a good sign, but diminishing cash tin be considered as a sign of trouble. But if plenty of cash is retained for many years, then investors should see why the management is not putting it into use. The reasons for maintaining a considerable amount as cash include direction's lack of interest in the investment opportunities, or maybe they are brusk-sighted, so they do non know how to utilize the cash. Even the cash flow analysis is done by the company to decide its source of cash generation and its awarding.
D) Inventories
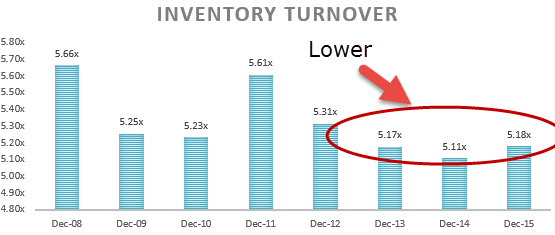
Inventories are the finished appurtenances accumulated by the visitor for selling them to its customers. The investor will see how much money is tied up by the company in its inventory. To analyze the inventory, a company calculates its inventory turnover ratio Inventory Turnover Ratio measures how fast the company replaces a current batch of inventories and transforms them into sales. Higher ratio indicates that the visitor's product is in high demand and sells chop-chop, resulting in lower inventory management costs and more earnings. read more , which is calculated every bit beneath:
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of appurtenances sold / Boilerplate inventory
Where,
- Price of goods sold The Toll of Goods Sold (COGS) is the cumulative total of direct costs incurred for the appurtenances or services sold, including direct expenses like raw material, directly labour price and other direct costs. However, it excludes all the indirect expenses incurred by the company. read more = Opening stock + purchases – Closing stock Closing stock or inventory is the amount that a company still has on its mitt at the end of a fiscal period. It may include products getting processed or are produced just not sold. Raw materials, work in progress, and last appurtenances are all included on a broad level. read more
- Boilerplate inventory Average Inventory is the mean of opening and endmost inventory of a detail period. It helps the management to understand the inventory that a business organisation needs to agree during its daily course of business concern. read more = (Opening inventory + Closing inventory) / 2
This ratio calculates how fast the inventory is converted into sales. A college inventory ratio Inventory ratio or inventory turnover ratio is an activity ratio that depicts the frequency of replacing the stocks sold by the company in a certain period. It is evaluated as the proportion of the toll of goods sold to the average inventory. read more shows that the appurtenances are sold quickly by the company and vice versa.
Eastward) Accounts Receivables

Accounts receivable is the money due to the debtors of the firm. Past analyzing accounts receivable, a visitor analysis the speed at which the amount is collected from the debtors.
For this, the company calculates the Accounts receivable turnover ratio, which is calculated every bit below:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Net credit sales/Average accounts receivable
Where,
- Net credit sales Net credit sales is the revenue generated from appurtenances or services sold on credit excluding the sales discount, sales allowance and sales return. It even amounts to the accounts receivables for a sure bookkeeping period. read more = Sales – Sales return – discounts
- Average accounts receivable = (Opening accounts receivable + endmost accounts receivable) / 2
This ratio calculates the number of times the visitor collects the boilerplate accounts receivable over a given period. College the ratio college is the efficiency of the company to collect its debtors A debtor is a borrower who is liable to pay a certain sum to a credit supplier such equally a bank, credit card visitor or goods supplier. The borrower could be an individual similar a dwelling house loan seeker or a corporate body borrowing funds for business expansion. read more than .
#2 – How to do Analysis of Liabilities on the Balance Canvas?
Liabilities include current liabilities and not-electric current liabilities. Electric current liabilities are obligations of the visitor to be paid inside a twelvemonth, whereas non-current liabilities are the obligations that are to be paid subsequently a twelvemonth.
A) Non-Current Liabilities

It can exist done past the debt to disinterestedness ratio The debt to equity ratio is a representation of the company'southward capital structure that determines the proportion of external liabilities to the shareholders' equity. It helps the investors determine the arrangement's leverage position and risk level. read more . The formula for the same is:
Debt to disinterestedness ratio =Long term debts/ Shareholders disinterestedness
- Where long term debts = debts to be paid off afterwards a year
- Shareholders equity Shareholder's equity is the residual interest of the shareholders in the visitor and is calculated as the difference betwixt Assets and Liabilities. The Shareholders' Equity Argument on the residue sheet details the change in the value of shareholder'due south disinterestedness from the start to the stop of an accounting period. read more = Equity share majuscule + preference share capital + accumulated profits
For example, Mania Inc. has its equity share upper-case letter amounting to $100,000. Its Reserves and surplus Reserves and Surplus is the amount kept aside from the profits that are to be used either for the business or for the shareholders to pay out dividends. Reserves and surplus is reflected under shareholders funds in the residual canvass. read more are $twenty,000, and the long term debts are $150,000
Therefore the debt to equity ratio = $150,000 / ($100,000 + $20,000) = 1.25:1
This ratio measures the proportion of the debt fund as compared to equity. Information technology helps to know the relative weights of the debts and the equity.
B) Current Liabilities
The current liabilities can as well be analyzed with the assist of the current ratio and the quick ratio The quick ratio, also known as the acid examination ratio, measures the ability of the company to repay the short-term debts with the help of the most liquid assets. It is calculated by adding full cash and equivalents, accounts receivable, and the marketable investments of the company, then dividing it by its total current liabilities. read more than . Both ratios are discussed in a higher place in the current avails section.
C) Equity
The amount of capital contributed Contributed majuscule is the corporeality that shareholders take given to the visitor for buying their stake and is recorded in the books of accounts as the common stock and boosted paid-in capital under the equity section of the company's rest canvas. read more past the shareholders is represented past the Equity and is too called as shareholder's equity. Equity is calculated by subtracting full liabilities from the total assets
Equity = Total Asset – Total Liabilities
At that place are various means in which disinterestedness can exist analyzed.
ROE
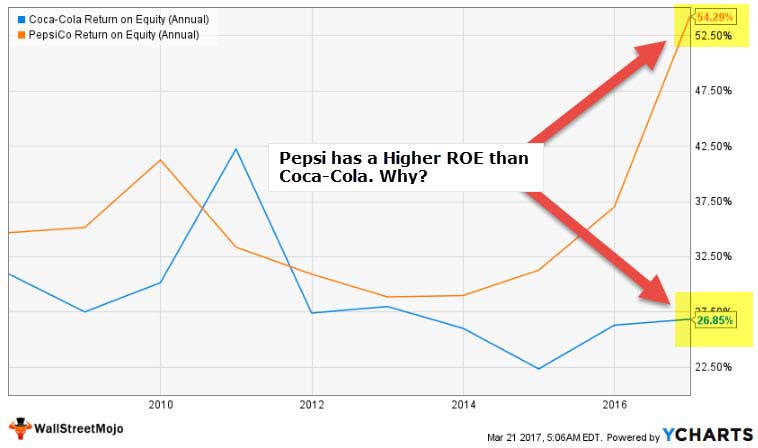
Return on equity Return on Equity (ROE) represents fiscal performance of a company. Information technology is calculated as the net income divided by the shareholders disinterestedness. ROE signifies the efficiency in which the visitor is using avails to make profit. read more an of import determinant which shows that company how the company is managing the capital of shareholder. Higher the ROE, improve information technology is for shareholders. It is calculated by dividing the internet income by the shareholder's equity.
For instance, XYZ had $xx million net income last year and shareholders' equity of $40 one thousand thousand terminal year, then.
ROE = $twenty,000,000/$40,000,000 = 50%
It shows that XYZ generated $0.fifty profit for every $ane of the equity of shareholders with ROE of fifty%.
Debt to Equity Ratio

Another ratio that helps analyze equity is the debt-disinterestedness ratio. The same is explained in case of non- current liabilities where Mania Inc, is having a debt-equity ratio of ane.25. The company has a higher debt-equity ratio as a debt of the company is more than the equity. A lower debt-disinterestedness ratio implies more financial stability. Companies having a higher debt-equity ratio, similar in the present example, are considered to be riskier to the investors and the creditors of the company.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Balance Sail Analysis. Here we talk over step past stride how to analyze residual canvass assets, liabilities, and equity along with examples and explanations. Yous may learn more about accounting from the following articles –
- Rest Sheet Ratios
- How to Read a Balance Sail?
- Examples of Balance Sheet
- Comparative Balance Sail
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/balance-sheet-analysis/
Belum ada Komentar untuk "The Balance Sheet Describes a Family's Financial Position:"
Posting Komentar